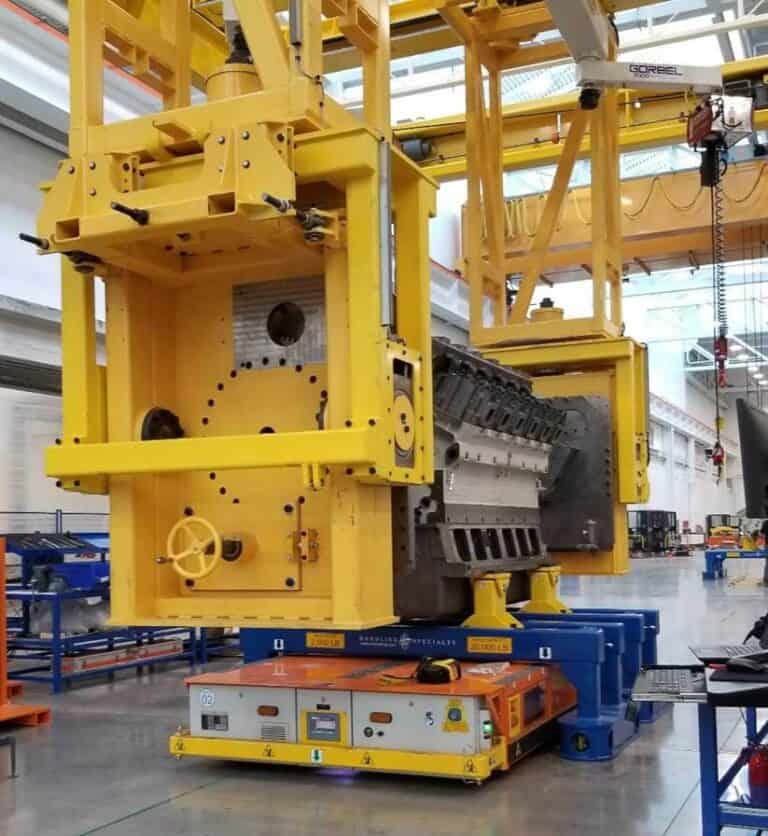
Overview of AGV Technology
The technology behind automated guided vehicles has become an integral part of modern assembly, manufacturing facilities, and MRO centers. These autonomous robotic vehicles are powered by cutting-edge technology, making them efficient, precise, and adaptable to various tasks. Below, we will delve into the core technologies that drive AGVs, their navigation systems, communication capabilities, control systems, sensors, energy sources, and software integration. We will also explore the current state of AGV technology and its promising future.
AGV Core Technology
Automated guided vehicles result from converging several core technologies that work together to ensure efficient operation. These include AGV operation technology, AGV navigation systems, AGV control systems, AGV sensors, AGV wireless communication, and AGV fleet management. Each AGV will draw on additional technologies to improve its customization to meet the industry’s requirements.
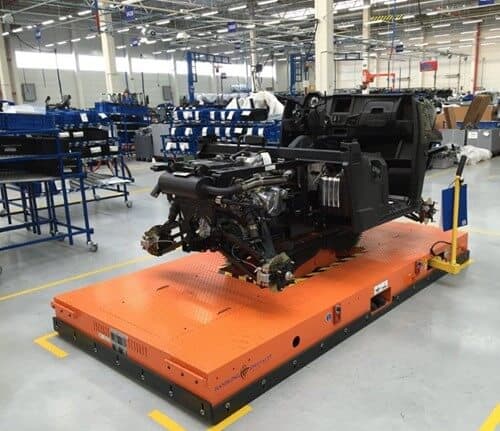

Navigation Systems
The ability of a custom AGV to navigate autonomously within a facility directly correlates with the critical aspects of AGV technology. AGVs employ various navigation systems, including:
- Laser navigation AGV: Utilizing laser scanners and reflectors, these AGVs create accurate maps of their surroundings and navigate using laser-based positioning, offering high precision and reliability.
- Inertial navigation AGV: These AGVs rely on onboard sensors like accelerometers and gyroscopes to calculate their position and orientation, allowing them to navigate with high accuracy even in challenging environments.
- Optical navigation AGV: This method uses optical cameras and sensors to identify markers or lines on the floor, guiding the AGVs along predefined paths.
Communication and Control Systems
Automated guided vehicles rely on wireless communication to coordinate their movements and share information with other machines and systems in the facility. Wi-Fi, RFID, and other wireless protocols ensure real-time data exchange, enabling seamless integration into the production or assembly environment.
Sophisticated AGV control systems manage their operations, including route planning, obstacle detection, speed control, and error handling. These systems ensure safe and efficient operation in dynamic environments.
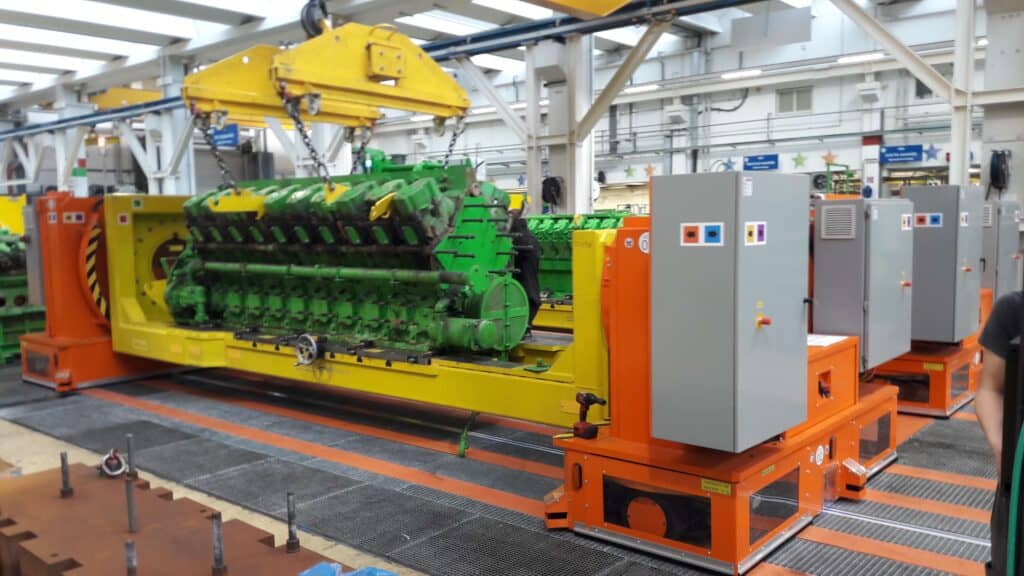

AGV Fleet Management
Coordination of a fleet of AGVs is a complex task in more extensive facilities. AGV fleet management systems oversee multiple vehicles, optimize routes, manage priorities, and ensure efficient resource utilization. These systems contribute to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
Sensors and Safety Features
To operate safely, AGVs are equipped with an array of sensors, including proximity, ultrasonic, and vision systems. These sensors detect obstacles, pedestrians, and other potential hazards, enabling AGVs to react and avoid collisions. AGV safety technology is essential for maintaining a secure working environment.
IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) automates an AGV fleet’s component wear and tear by alerting operations before any maintenance issues or part changes are required, avoiding costly downtime. Monitoring battery life and scheduling charging times also advances AGV automation technology. These efficiency sensors are critical in AGV performance optimization, tracking variables such as motor temperature, cargo weight, and component vibrations. By continuously collecting data, AGVs can make real-time adjustments to maximize their efficiency and extend operational uptime.
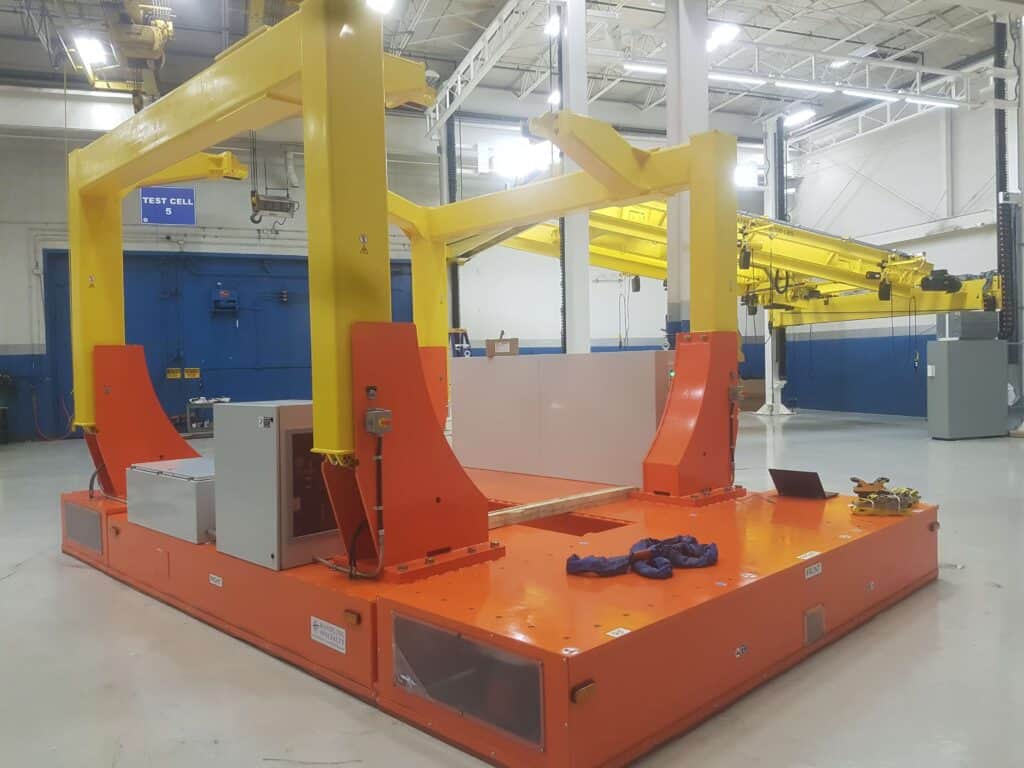

Software and Integration
Integrating automated guided vehicle software with existing assembly or manufacturing systems is crucial for seamless operation. AGV system software ensures efficient communication between AGVs and other equipment, such as conveyor belts, storage systems, and robots, streamlining overall operations.
Power and Energy Systems
AGVs are powered by various energy sources, with AGV batteries being the most common. To enhance energy efficiency, AGVs are designed to recharge autonomously through technologies like inductive charging. This innovation ensures that AGVs can operate continuously without manual battery swaps, reducing downtime.
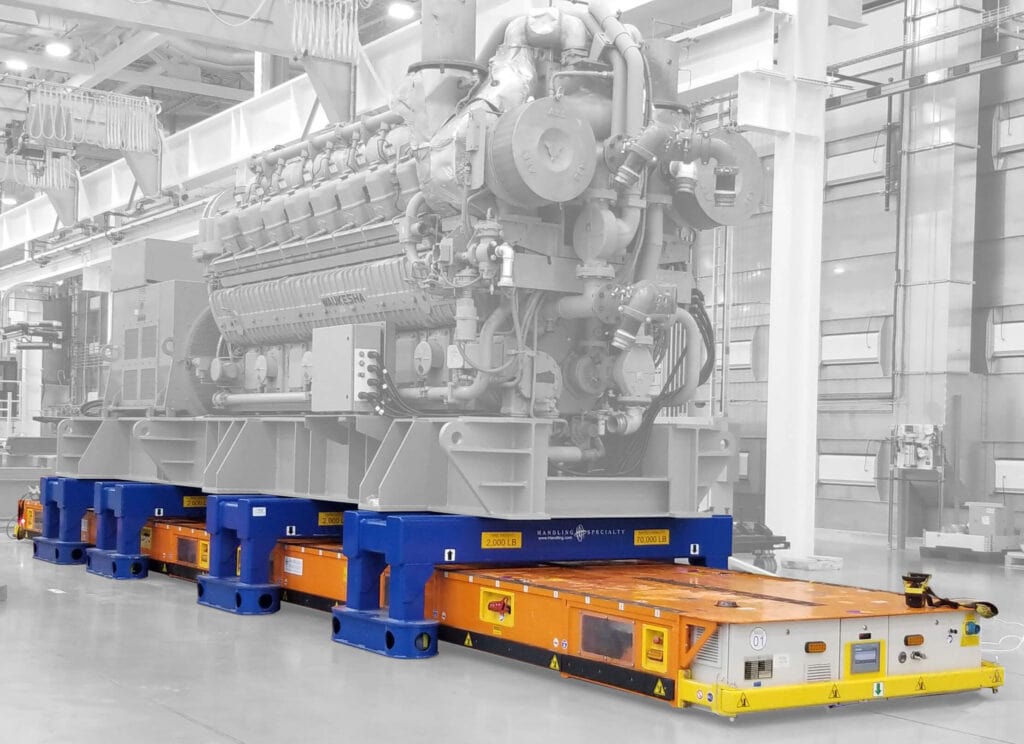

Technology in AGV Development and Future Advancements
The technology behind AGVs continues to evolve rapidly. Advances in AI and machine learning hold promise for the future, allowing AGVs to adapt to changing environments and tasks more efficiently. Enhanced safety features, improved energy efficiency, and increased payload capacities are also on the horizon.
Conclusion
Automated Guided Vehicles have come a long way, thanks to their core technologies, navigation systems, communication capabilities, control systems, sensors, custom tooling and accessories, and software integration. As AGVs continue to advance, they play a crucial role in enhancing productivity and safety in various industries. The future of AGV technology is bright, promising even more innovation and efficiency in material handling and logistics.