Introduction to Automated Guided Vehicles Types
Several types of Automated Guided Vehicles have transformed industries across the globe by automating material handling processes. These intelligent robotic vehicles are designed to transport materials within factories, warehouses, and other facilities with precision and efficiency. AGVs have become indispensable in modern manufacturing and logistics, offering various types and applications.
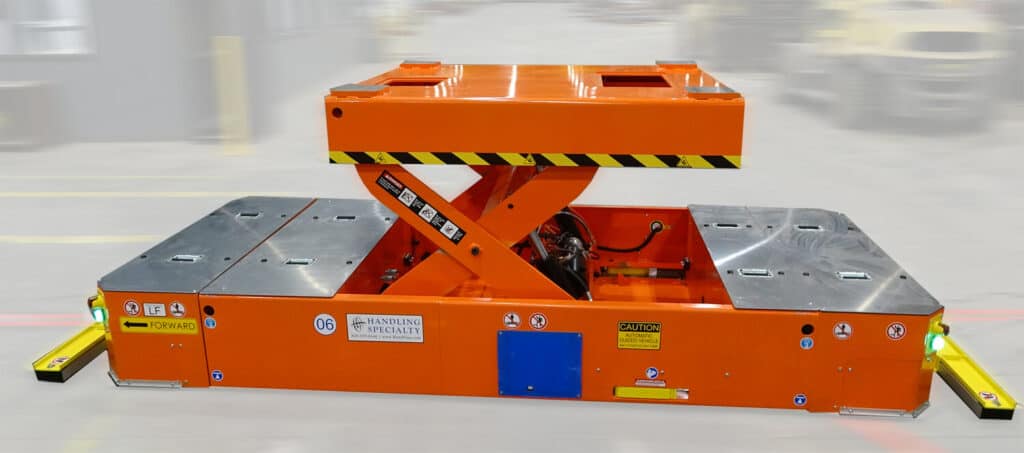

Types of Automated Guided Vehicles
Types of automated guided vehicles come in various forms, each tailored to specific tasks and environments. Some common AGV types include:
- Laser-guided AGVs: These vehicles use laser technology to navigate and avoid obstacles, making them highly adaptable to changing environments.
- Magneticly-guided AGVs: These AGVs follow a predetermined path marked by magnetic tapes on the floor, ensuring precise movement.
- Vision-guided AGVs: Equipped with cameras and advanced computer vision technology, these AGVs can navigate dynamically and adapt to their surroundings.
Automated Guided Vehicle Design Significance
The design of AGVs plays a crucial role in their effectiveness. Their compact and efficient design allows them to operate in tight spaces and optimize material flow within a facility. Customizable designs ensure that AGVs can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries.
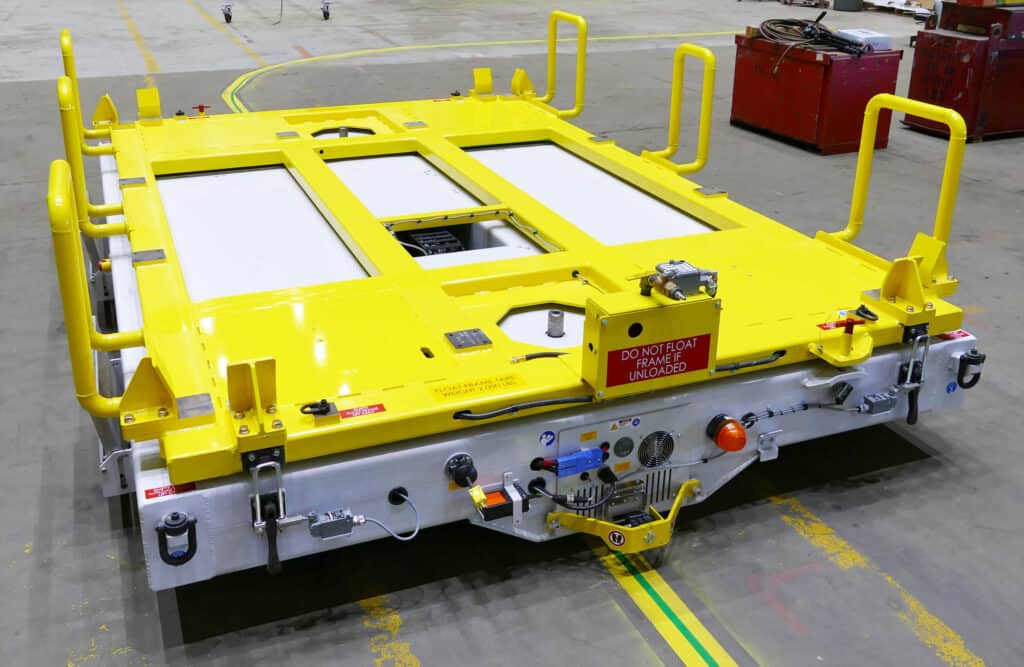

AGV Navigation Technology
AGVs rely on advanced navigation technologies to move autonomously. These technologies include GPS, laser scanners, cameras, and sensors. AGVs can make real-time decisions to avoid collisions and optimize routes by continuously monitoring their surroundings.
AGV in Manufacturing, Assembly, and MRO
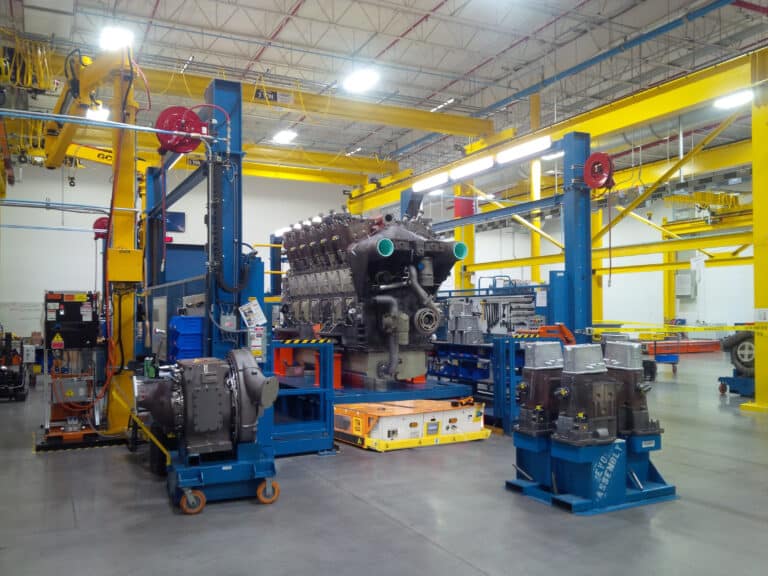
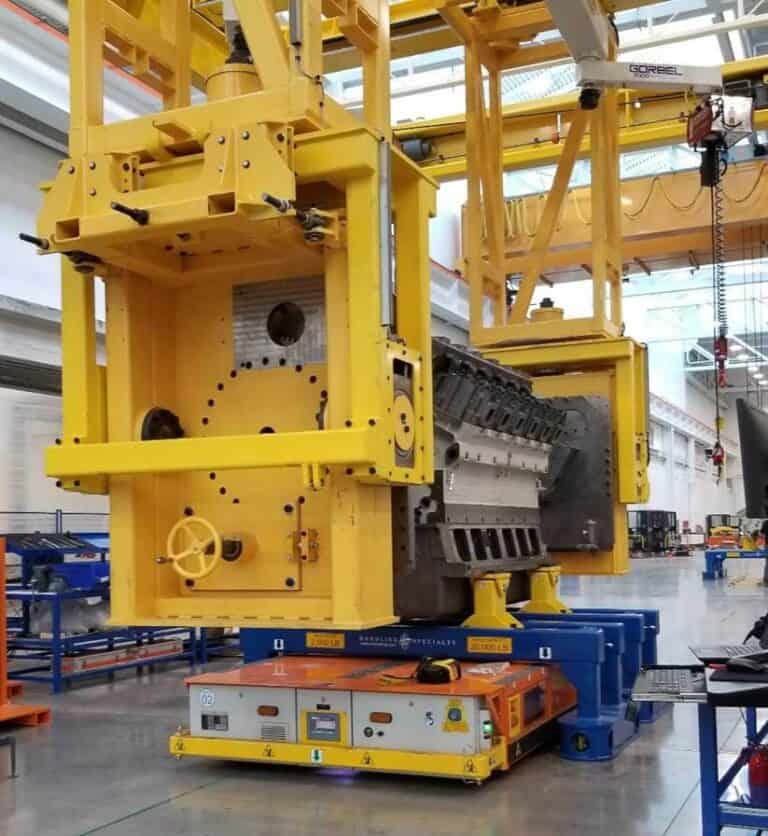
In the manufacturing industry, AGVs are used for tasks such as material transport, assembly line replenishment, and machine tending. They enhance efficiency, reduce human labor, and ensure consistent production processes. Customized tooling and optional equipment are essential for your automated guided vehicle when considering product size, shape, capacity, and application requirements.
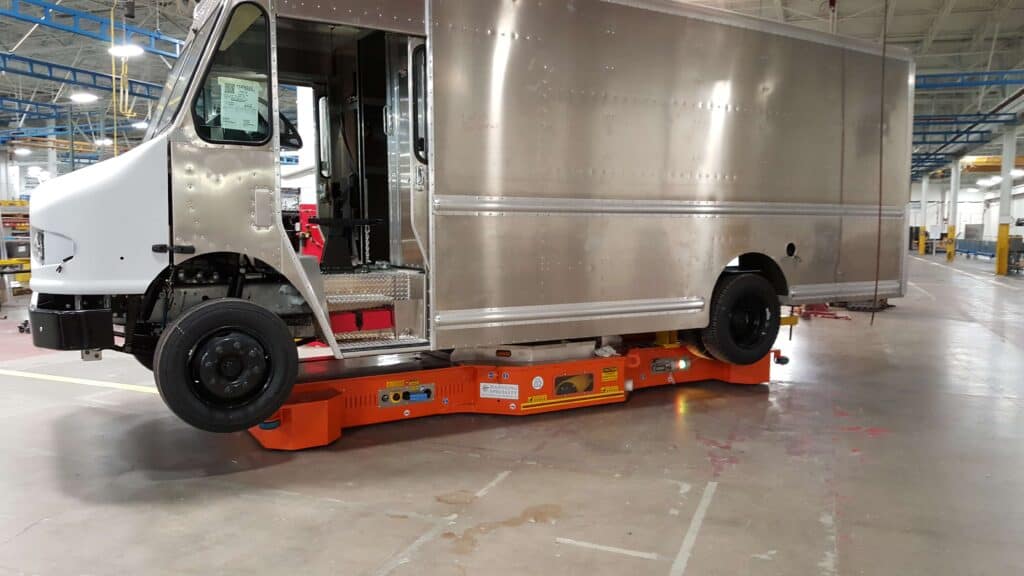

Case Studies of AGV Implementation
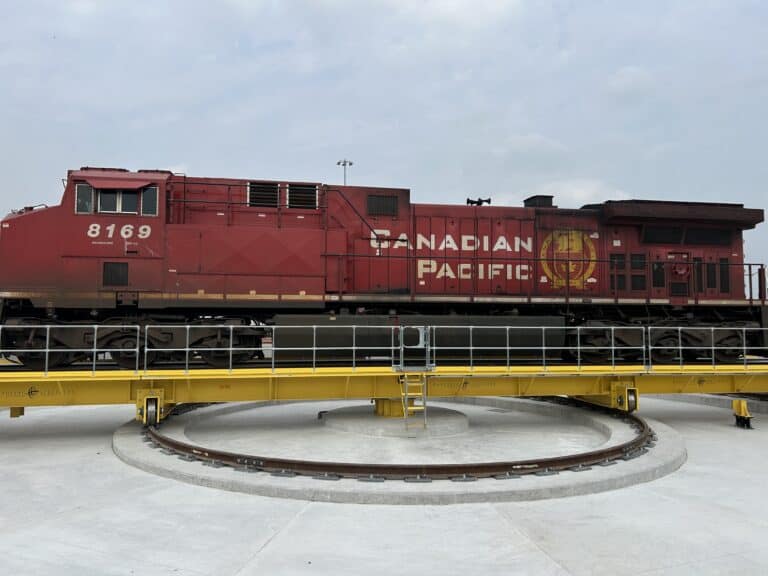
AGVs have applications in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, advanced manufacturing, power generation, iron and steel, and rail and transportation. Their versatility makes them suitable for heavy-duty tasks and delicate material handling processes.
Automated Guided Vehicle Deployment Examples
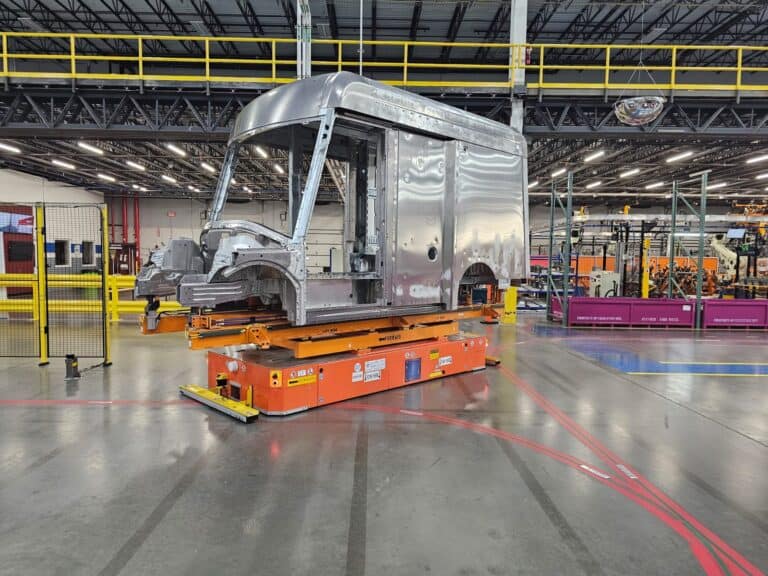
AGV implementations include transporting raw materials to production lines, moving finished products to storage or shipping areas, and moving products through work cells as technicians assemble, repair, or maintain the merchandise. AGVs can also work collaboratively with human operators in shared spaces.
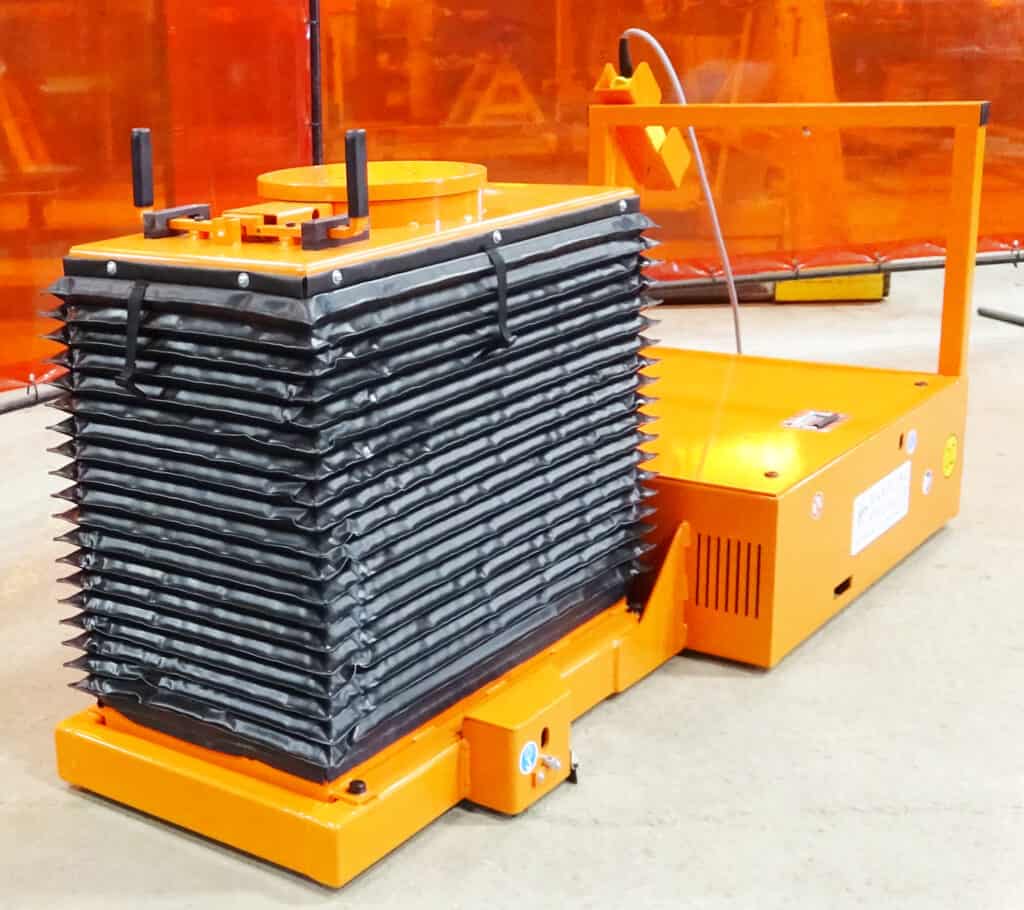

AGV Implementation Benefits
The implementation of AGVs brings numerous advantages, including:
- Increased productivity and efficiency
- Reduction in labor costs
- Improved safety with collision avoidance systems
- Accurate tracking and tracing of materials
- Scalability to meet growing demands
- 24/7 operation capabilities
Real-World AGV Case Studies
Handling Specialty has several detailed case studies from industry sectors, such as automotive AGVs, power generation AGVs, Process Industry AGVs, Aerospace AGVs, Iron and Steel shop AGVs, and many more. Please review our website for information and examples of AGVs in application. Each AGV was custom-designed with specialized tooling and options like scissor lifts and rotators to best position equipment while moving through the assembly or MRO processes.
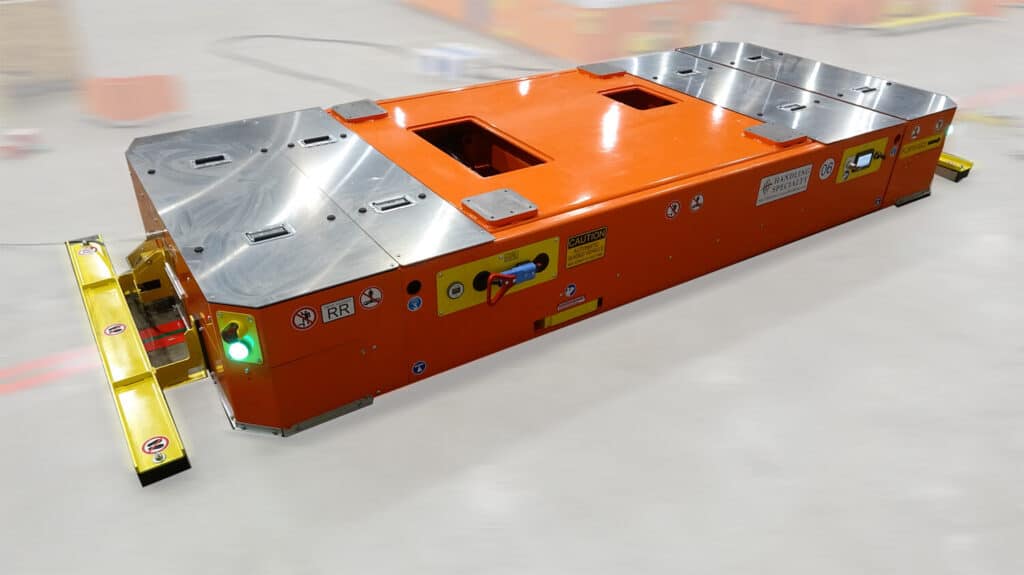

Innovations in AGV Design
Recent advancements in AGV technology have introduced features like enhanced AI algorithms for path optimization, improved battery life, IIoT for predictive maintenance, and increased payload capacity. These innovations continue to expand the scope of AGV applications.
AGV designs have evolved over the years, becoming more compact, robust, energy-efficient, and versatile. This evolution allows AGVs to adapt to diverse operational requirements, making them an even more valuable asset.
Automated Guided Vehicle Implementation Challenges and Solutions
While AGVs offer numerous benefits, they pose challenges, such as initial setup costs, integration with existing systems, and maintenance. These challenges can be addressed through careful planning, proper training, and regular maintenance routines. ROI of a customized AGV system often pays for itself within a short window, saving facilities money in the long term.
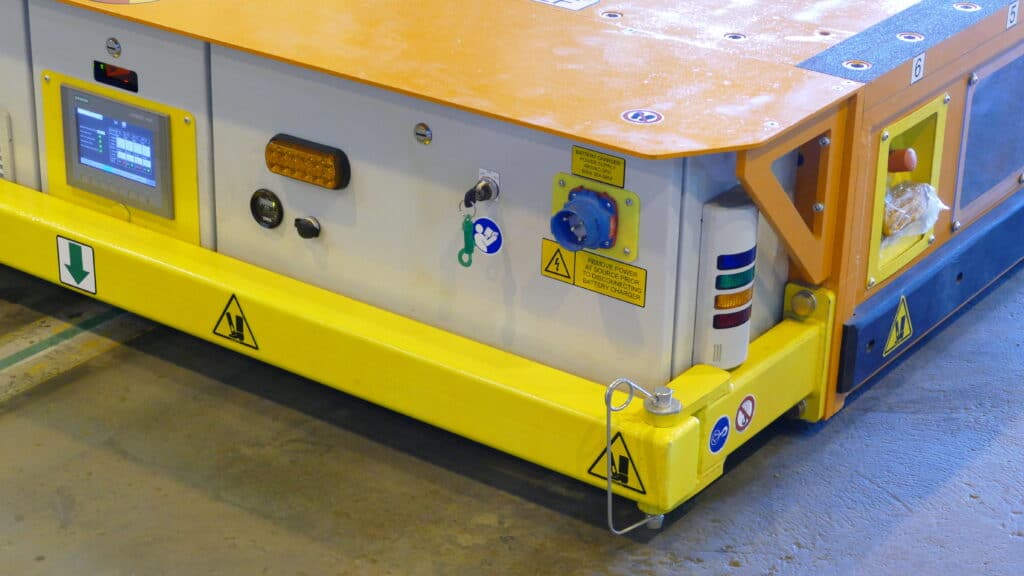

AGV Best Practices
To maximize the benefits of AGVs, best practices such as regular system monitoring (IIoT), staff training, and continuous improvement in navigation algorithms are essential.
AGVs are versatile tools that can be adapted for various applications and industries. Their ability to perform multiple tasks makes them a valuable asset in an ever-changing business landscape.
The future of AGVs looks promising, with ongoing research and development focused on improving navigation, energy efficiency, and automation capabilities. AGVs are expected to play a vital role in the growth of Industry 4.0.
Conclusion
The AGV sector is poised for substantial growth as industries increasingly recognize the benefits of automation. AGVs have the potential to revolutionize material handling processes across various sectors.
Since their inception, automated guided vehicles (AGVs) have revolutionized material handling processes across industries. Their versatility, efficiency, customization, and adaptability make them an essential tool for modern manufacturing, MRO, and assembly. With ongoing innovations and expanding applications, AGVs are set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of automated material handling.