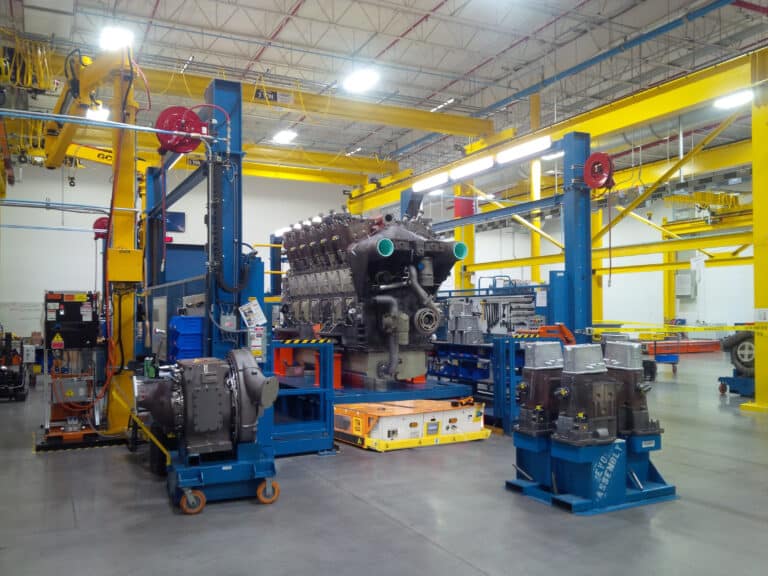
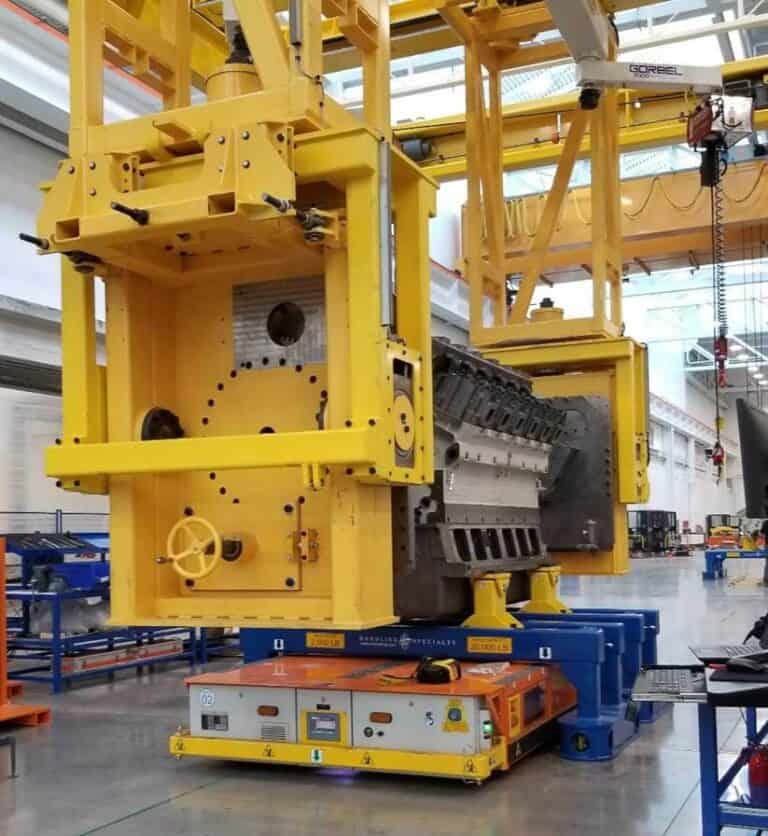
What is an automated guided vehicle system? An AGV system, or automated guided vehicle system, otherwise known as an automatic guided vehicle, autonomous guided vehicle or even automatic guided cart, is a system which follows a predestined path around a facility. An AGV automated guided vehicle is a mechanical vehicle which carries a load through either an assembly, manufacturing or warehousing facility.

Types of automated guided vehicles
- Automated Guided Carts
An AGC is a basic AGV with limited automation where it follows a painted strip on the floor to move on a pre-determined path to perform repetitive action. AGV carts are often used in sorting, storage and cross-docking applications to reduce labour costs. - Unit Load Carriers
These AGV transfer carts are designed to carry specific parts or products with engineered tooling to carry a pallet or tote loaded with multiple items. - Heavy Towing Carriers
These heavy-load AGVs are used for transporting heavy loads over longer distances within a large facility without the assistance of an operator following a set path. This path can be altered simply by reorienting the floor tape or paint it follows. - Forklift and Towing AGVs
Towing AGVs are automated guided vehicle robot carts designed to act as stock robots for warehousing, pulling orders from heights with forks or other special tooling created for the specific application. - Tugger AGVs
A tugger AGV pulls heavy loads from point A to point B employing trailers filled with products or parts. These tugger-automated guided vehicles can have several pre-determined stops while moving through a plant or factory or warehouse.
Automated Guided Vehicles Working
An industrial automated guided vehicle working principle is built to withstand very heavy loads as in Truck Outfitting assembly plants, which carry the frame through the assembly process. These AGVs almost always require a custom design with tooling options in order to work with the assembly or manufacturing plant’s specific applications.
AGV Navigation Control
No longer are plc-based automatic guided vehicles built to follow fixed tracks which were traditionally built into the floor of a facility to guide the vehicles, but rather magnetic tape or QR-coded tape via the AGVs laser guidance system. Unlike tracks built into the floor, the tape allows for easy and affordable reconfiguration of the facility’s floor operations.
AGV Steering Control
AGV systems have several drive motors to allow for specialized steering such as zero-radius turning, diagonal, left, right, backward and forward movement, which offers extraordinary maneuverability within any factory space. AGVs are battery operated, which also include a manual option for bringing the vehicle off the line for charging or maintenance tasks. They are usually fitted with motion stop sensors and kick stops for added safety. Each AGV is programmed to follow a course set by the QR-coded tape as well as obey pre-programmed speeds further to customize the client’s specific applications and assembly needs.
AGV Traffic Control
An AGV system is designed with multiple safety features which offer exceptional traffic control within a facility through collision-avoidance capabilities with the use of audible and visual alarms, motion sensors, E-Stops, and laser guidance. An automatic guided vehicle is an excellent addition to any busy operation in the manufacturing industry. Benefits include heightened safety, ergonomics, efficiency and flexibility in floor layout design. An AGV can be built to hold and carry virtually any weight capacity, and with advancements in motion control, the AGV of the future is already here.
Where are Automated Guided Vehicles Used?
Industrial AGV systems are built for multiple industries, including automotive assembly, aerospace manufacturing, food processing, beverage, chemical, commercial printing, hospitals, newspaper, paper, pharmaceutical, plastics, and warehousing and distribution facilities.
Benefits of using AGVs
AGVs offer exceptional accountability once a product is loaded onto an AGV, minimizing misplaced product. Where labour costs tend to increase and change quickly depending on multiple conditions, an automated guided vehicle system’s costs can be very predictable, and its path changes as production and handling needs evolve.
Additionally, AGVs eliminate access issues created by conveyors and require less space than conventional forklifts, allowing for narrower aisles and increasing storage space within a facility. Battery charging & handling can be automatic with an AGV system, minimizing wear on components.
Automated Guided Vehicles have smooth acceleration/deceleration, handle products gently, reduce product damage, perform repetitive movement tasks predictably; and because of their reliability AGVs improve scheduling capabilities and the efficiency of operations while additional AGVs can be added to expand capacity and throughput in any assembly, manufacturing or warehousing operation.
For examples of an industrial AGV in application, you can visit Handling Specialty’s Youtube pages and learn more about the AGV system on the website’s AGV Case Studies.