Unlocking Production Line Efficiency: The Indispensable Role of Automated Guided Vehicles
Introduction: The Evolution of Production Lines and the Call for Efficiency
The manufacturing production line is under constant pressure to be faster, more flexible, and more cost-effective. The era of predictable, static assembly processes is giving way to a new reality defined by fluctuating consumer demand, complex supply chains, and the strategic push toward localized manufacturing. This evolution demands a fundamental shift from traditional, labor-intensive material handling to intelligent, automated systems that can keep pace with modern production needs.
The Modern Manufacturing Imperative: Navigating Demand Volatility, Reshoring, and Cost Pressures
Modern manufacturing facilities face a triad of challenges. Demand volatility requires production lines that can quickly adapt to changing product mixes and volumes. AGVs are an excellent capital expense when looking to optimize factory space and alter manufacturing processes. Automated Guided Vehicles allow for flexibility in the manufacturing lines as needed. Additionally, the trend of reshoring brings production closer to home but often involves higher labor costs, necessitating extreme operational efficiency. Simultaneously, relentless cost pressures demand the elimination of waste, bottlenecks, and non-value-added activities at every stage of production. Manual material handling, with its inherent limitations in speed, consistency, and safety, has become a primary bottleneck in achieving the agility required to thrive.
Introducing Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Redefining Material Transport and Logistics
Enter Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs). These intelligent, self-guided robots are engineered to transport materials reliably and efficiently throughout a factory or warehouse. By taking over the repetitive and often strenuous tasks of moving raw materials, work-in-progress (WIP), and finished goods, AGVs introduce a new level of precision, predictability, and automation to internal logistics. They are the circulatory system of the modern factory, ensuring that the right materials are in the right place at the right time, every time.
Article Focus: Why AGVs are Not Just Beneficial, but Indispensable for Optimizing Production Lines
While the benefits of automation are widely understood, this article will argue that for the modern production line, AGVs have moved beyond a beneficial upgrade to become an indispensable component of a competitive manufacturing strategy. We will explore their core functions, their direct impact on key efficiency metrics, the technology that powers them, and the strategic framework for their successful implementation. We will demonstrate how these advanced robots are foundational to building the resilient, efficient, and future-proof production lines of tomorrow.
Understanding Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in a Production Context
To appreciate their indispensable role, it’s crucial to understand what AGVs are, the different forms they take, and how they differ from other mobile robots. This clarity helps in selecting the right automation for specific production needs.
An Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) is a portable robot that follows marked lines on the factory floor, or uses vision, magnets, or lasers for navigation. Unlike manually operated forklifts, AGVs operate autonomously within a defined, structured environment. Their primary purpose is to automate material handling tasks, providing a consistent and reliable flow of materials within a factory. AGV systems are ideal for repetitive point-to-point movements, which are common along an assembly line.
Key Types of AGVs Tailored for Production Line Needs
AGVs come in various forms, each designed for specific tasks on the production floor:
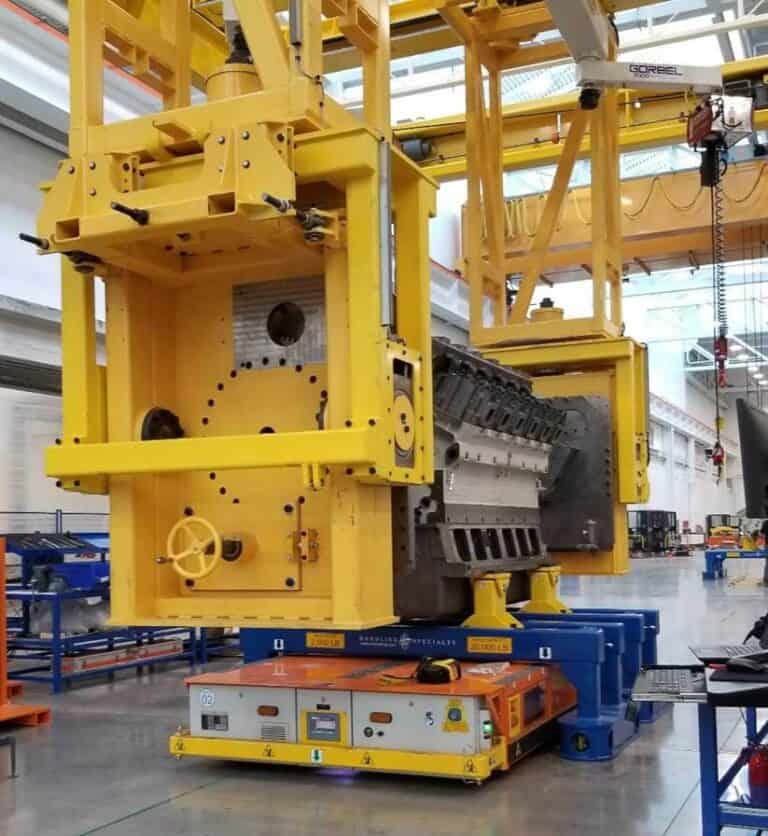
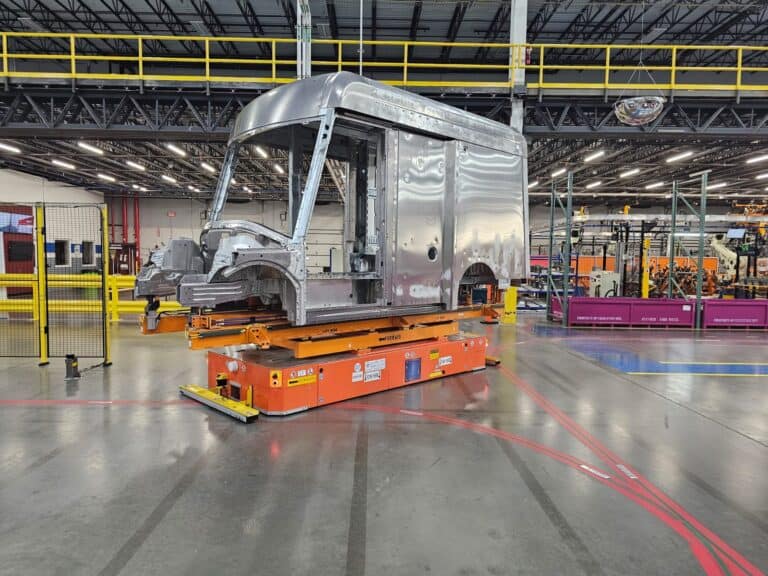
- Assembly Line AGVs: These specialized vehicles carry a sub-assembly or the main product body from one station to the next, acting as a mobile assembly platform. These AGVs can be custom designed for a specific application including tooling that carries, lifts, tilts, or rotates the product to pre-determined positions per work cell.
- Tugger AGVs: These robots tow a train of non-powered carts, efficiently moving multiple loads at once, ideal for line-side replenishment or “milk-run” logistics.
- Unit Load AGVs: Designed to carry single items like pallets, bins, or large components on their deck, these are workhorses for transferring WIP between workstations.
- Forklift AGVs: These automate traditional forklift tasks, such as picking up and placing pallets from racks or the floor, seamlessly integrating with existing pallet-based infrastructure.
The Indispensable Impact: How AGVs Drive Core Production Line Efficiency
AGVs are more than just transport vehicles; they are catalysts for systemic efficiency improvements that impact nearly every aspect of the production process. Their deployment creates a cascade of benefits that are foundational to lean manufacturing and smart factory principles.
Streamlining Material Flow and Work-in-Progress (WIP) Movement
The most immediate impact of AGVs is on material flow. They eliminate the delays and inconsistencies associated with manual transport. By delivering raw materials just-in-time to the first station and moving WIP seamlessly between subsequent stations, AGV systems drastically reduce idle time. This ensures that machinery and operators are never waiting for parts, which minimizes bottlenecks and keeps the entire production line moving at a steady, optimized pace.
Enhancing Assembly Line Throughput and Consistency
On the assembly line, consistency is paramount. AGVs deliver components with unwavering precision and timing, supporting a rhythmic and predictable workflow. In some applications, an AGV can serve as the mobile platform for the product itself, moving it from one robotic or human workstation to the next. This automated transport standardizes cycle times between stations, leading to a significant increase in overall throughput and improved product quality due to the reduction in manual handling errors.
Boosting Safety and Mitigating Risks in Busy Manufacturing Plants
Manufacturing floors can be hazardous environments. AGVs fundamentally improve safety by reducing the reliance on manually operated forklifts, a common source of workplace accidents. Equipped with advanced sensors, scanners, and emergency stops, AGVs are designed to navigate safely around people and infrastructure. Their programmed, predictable paths create a more organized and secure factory floor, minimizing the risk of collisions and injuries. This, is turn, minimizes equipment damage and downtime.
Optimizing Space Utilization and Production Layout Flexibility
Traditional material handling solutions like conveyors are fixed and occupy significant floor space. AGV systems operate on the existing factory floor, requiring minimal infrastructure changes. This frees up valuable space and provides unparalleled flexibility. Production lines can be reconfigured more easily to accommodate new products or changes in process flow, as the AGV paths can be reprogrammed without costly physical alterations. This adaptability is critical for agile manufacturing. Additionally, a factory can add more AGVs to its production line if required.
Providing Data for Continuous Improvement and Smart Factory Integration
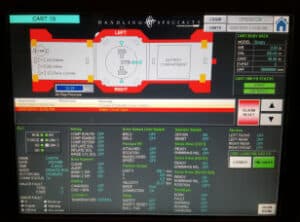
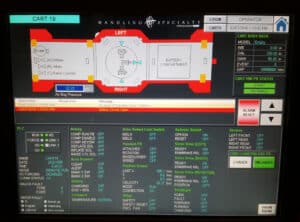
Modern AGV systems are mobile data hubs. They continuously collect operational data on travel times, load status, battery levels, and downtime. This information, when fed into a fleet management system or Manufacturing Execution System (MES), provides valuable insights into production line dynamics. Managers can use this data to identify hidden inefficiencies, optimize routes, and make informed decisions for continuous process improvement, laying the groundwork for a truly data-driven smart factory.
The Technology Behind the Efficiency: Advanced AGV Systems and Capabilities
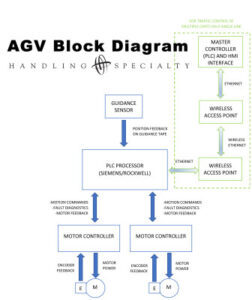
The reliability and efficiency of an AGV are not accidental; they are the result of a sophisticated integration of navigation, control, power, and sensing technologies. Understanding these components reveals how AGVs achieve such a high level of performance.
Robust Navigation and Guidance Systems for Precision and Reliability
The navigation system is the heart of an AGV. Different technologies suit different environments:
- Magnetic Tape/Spot Navigation: AGVs follow a magnetic tape laid on the floor. It is a reliable and cost-effective method for simple, fixed routes.
- Laser Guidance: The AGV uses a rotating laser to detect reflective targets mounted on walls. This system offers high precision and allows for more complex pathing that can be easily modified.
- Vision Guidance: Cameras capture features of the facility to navigate, offering flexibility without the need for physical infrastructure like reflectors or tape.
Intelligent Fleet Management and Control Systems
A single AGV is useful, but a fleet of them working in concert is transformative. The fleet management system is the central brain that orchestrates the entire operation. It receives transport orders, assigns tasks to the most appropriate AGV, manages traffic flow to prevent congestion, and interfaces with other factory systems like WMS or ERP. This intelligent control ensures the entire AGV system operates as a cohesive and optimized unit.
Power Management and Automated Charging
To ensure continuous operation, AGVs employ sophisticated power management strategies. Most modern systems feature automated charging. When an AGV’s battery level drops below a certain threshold, it will automatically complete its current task and navigate to a charging station. Some use opportunity charging, where AGVs receive quick power boosts during short idle periods in their workflow, maximizing uptime and ensuring 24/7 availability.
Sensors, Artificial Intelligence, and Predictive Maintenance
Safety and operational awareness are guaranteed by an array of onboard sensors. LiDAR and infrared sensors detect obstacles, while encoders and gyroscopes ensure precise movement and positioning. Increasingly, AI algorithms are being integrated to improve navigation efficiency and decision-making. These sensors also collect performance data on motors and other components, enabling predictive maintenance alerts that help prevent unexpected downtime before it occurs.
Strategic Implementation: Unleashing AGV Potential on Your Production Line
Deploying AGVs is a strategic initiative that requires careful planning and execution. A well-thought-out implementation process ensures that the technology delivers maximum return on investment and seamlessly integrates into existing operations.
Assessing Your Production Line’s Readiness for AGVs
The first step is a thorough analysis of your current processes. Identify repetitive, predictable material handling tasks that create bottlenecks or pose safety risks. Map out material flow paths, measure transport distances and frequencies, and quantify the costs associated with current methods. This data will build the business case and define the specific requirements for an AGV system. An AGV OEM like Handling Specialty, will have professionals to guide your facility mapping and assist in choosing the right custom AGV for your application needs.
Planning and Design: From Simulation to Deployment
Once readiness is confirmed, the planning phase begins. This involves selecting the right type of AGV and navigation technology for your application. Working with an integration partner, you can use simulation software to model the AGV system’s performance within your factory layout. This allows you to optimize routes, determine the required number of vehicles, and validate the expected efficiency gains before a single robot is deployed.
Seamless Integration with Existing Infrastructure
A key consideration is integrating the AGV system with your existing infrastructure. This includes not only the physical environment (floor condition, aisle widths, doorway clearances) but also your software ecosystem. The AGV fleet manager may communicate with your MES or WMS to receive transport orders and provide real-time status updates, creating a truly connected and automated workflow.
Calculating the Return on Investment (ROI) and Measuring Success
The ROI for AGVs extends beyond direct labor savings. It includes gains from increased throughput, reduced product damage, improved safety (leading to lower insurance costs), and minimized downtime. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established before deployment—such as cycle time, WIP levels, and throughput—and measured afterward to quantify the project’s success and identify areas for further optimization.
Addressing Challenges: From Initial Setup to Ongoing Optimization
Implementation challenges can range from network connectivity issues to employee apprehension. A phased rollout can help manage the initial setup. Proper training and change management are crucial to ensure employees understand the benefits of the new system and how to work alongside the AGVs safely and effectively. The process doesn’t end at deployment; ongoing optimization based on performance data is key to maximizing long-term value.
The Future-Proof Production Line: AGVs as a Catalyst for Industry 4.0 and Agile Manufacturing
Automated Guided Vehicles are not merely an endpoint in automation; they are a foundational technology that enables the broader vision of the smart, agile factory of the future.
AGVs in Smart Factories: Hyper-Connectivity and Intelligence
In an Industry 4.0 environment, AGVs act as the physical link in a hyper-connected system. They receive instructions from an intelligent MES, transport materials to smart workstations, and communicate their status in real-time. This connectivity allows for unprecedented visibility and control over the entire production process, enabling real-time adjustments and autonomous decision-making.
Human-Robot Collaboration: A Synergistic Workforce
The future of manufacturing is not about replacing humans but empowering them. AGVs handle the monotonous, physically demanding transport tasks, freeing human workers to focus on higher-value activities that require critical thinking, dexterity, and problem-solving skills, such as quality assurance, complex assembly, and system maintenance. This creates a synergistic workforce where humans and robots each perform the tasks they are best suited for.
Green Technology and Sustainable Manufacturing with AGVs
Modern AGVs are predominantly electric, contributing to a reduction in the carbon footprint compared to fossil-fuel-powered vehicles. Their optimized routing and efficient operation also reduce energy consumption. By enabling just-in-time material flow, they help minimize waste and the need for large buffer inventories, supporting the principles of lean and sustainable manufacturing.
Conclusion
The modern production line is an ecosystem where speed, precision, and adaptability are the currencies of success. In this demanding environment, Automated Guided Vehicles have proven to be an indispensable asset. They are no longer a futuristic concept but a practical, powerful tool for streamlining material flow, boosting throughput, enhancing safety, and providing the data-driven insights needed for continuous improvement. By automating the critical-yet-non-value-added task of material handling, AGVs unlock the full potential of both machinery and human talent. For any manufacturer seeking to build a resilient, competitive, and future-proof operation, the strategic implementation of AGV systems is not just an option—it is a necessity. The journey begins with assessing your unique production needs and exploring how this foundational automation can drive your facility toward a new era of efficiency.